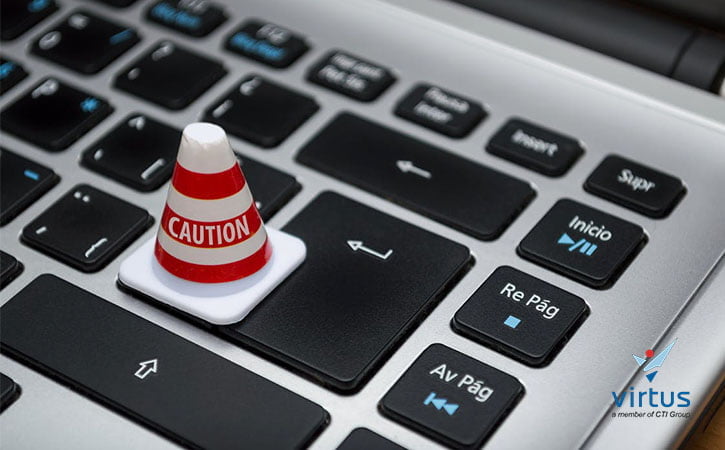
With the increasing scale of data breaches and hacks we’ve seen recently everyone is asking Why data protection is important. Data Protection has become more important than ever, a hacker took control of a hotel’s key card system, locking guests in their room until a ransom was paid, etc.
Data privacy laws and regulations vary from country to country and even from state to state, and there's a constant stream of new ones. For Example, on May 25th was a big day for IT professionals in the European Union (EU) and, more importantly, anyone involved in IT with companies processing goods or services to EU residents, even if those companies are operating from outside the EU. The European Union (EU) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a new regulation ([EU] 2016/679) intended to strengthen and unify data privacy rights for European Union data subjects. It builds upon and updates the current EU data protection framework.
GDPR export privacy standards at worldwide, many organizations will be required to go through large-scale business process changes as they put policies in place to protect personal data. The efforts involved in supply chain management, vendor assessment, process and policy changes, and technology enhancements raise a broad scope of questions.
Below are some summaries of high-risk GDPR obligations that can be focused for Data Protection:
- Data security and incident management requires an organization to have appropriate technical and organizational security controls and procedures in place to ensure the secure processing of an individual’s personal data as well as notify individuals and/or an EU supervisory authority in the event of a data breach.
- Record keeping requires an organization to maintain records of their processing activities, which extends to any vendor that they engage, as well as to document the data protection impact assessment that they have undertaken.
- Accountability principle essentially means an organization must demonstrate that they comply with the GDPR data protection principles.
- Data retentionis key to ensuring fair processing. Personal data should not be retained for longer than necessary in relation to the purposes for which the data is collected or for which it will be further processed.
- Data minimization means that companies should only collect and use data in a manner that is consistent with a legitimate business purpose and consistent with the notice provided to the data subject.
- Data subject rights grant individuals the right to access, correct or erase their personal data upon request. An organization must respond to the individual’s request within one month.
For a global organization, experts recommend having a data protection policy that complies with the most stringent set of rules the business faces, while, at the same time, using a security and compliance framework that covers a broad set of requirements. “Data protection is not a luxury but a necessity, not only for the functioning of our democracies but also for the protection of our citizen and the success of our data-driven economies" a quote from V?ra Jourová, European Commissioner for Justice, Consumers and Gender Equality.